Nanorobotics
m (Removing a "New"-icon) |
m (→External Links) |
||
| Line 43: | Line 43: | ||
=External Links= | =External Links= | ||
| − | * Sheffield Hallam University | + | * Project Partners |
| − | ** [http://vision.eng.shu.ac.uk/mediawiki2/index.php?title=Special:Userlogin&returnto=Main_Page Nanorobotics/MMVL shared private Wiki] | + | ** Sheffield Hallam University |
| − | ** [http://vision.eng.shu.ac.uk/mediawiki3/index.php?title=Special:Userlogin&returnto=Main_Page MMVL only section] | + | *** [http://vision.eng.shu.ac.uk/mediawiki2/index.php?title=Special:Userlogin&returnto=Main_Page Nanorobotics/MMVL shared private Wiki] |
| − | * University of Sheffield | + | *** [http://vision.eng.shu.ac.uk/mediawiki3/index.php?title=Special:Userlogin&returnto=Main_Page MMVL only section] |
| − | ** [http://www.shef.ac.uk/moebus/nanomanipulation.html Project announcement] | + | ** University of Sheffield |
| − | ** [http://www.shef.ac.uk/eee/research/fegtem/ University of Sheffield Engineering Faculty FEGTEM] | + | *** [http://www.shef.ac.uk/moebus/nanomanipulation.html Project announcement] |
| − | ** Publication ''[http://eprints.iisc.ernet.in/archive/00004227/ Indentation mechanics of Cu-Be quantified by an in situ transmission electron microscopy mechanical probe]'' | + | *** [http://www.shef.ac.uk/eee/research/fegtem/ University of Sheffield Engineering Faculty FEGTEM] |
| − | ** '''[http://nano.group.shef.ac.uk/ Nanorobotics group]''' at Sheffield University (project leader) | + | *** Publication ''[http://eprints.iisc.ernet.in/archive/00004227/ Indentation mechanics of Cu-Be quantified by an in situ transmission electron microscopy mechanical probe]'' |
| − | * University of Nottingham | + | *** '''[http://nano.group.shef.ac.uk/ Nanorobotics group]''' at Sheffield University (project leader) |
| − | ** [http://www.nottingham.ac.uk/physics/ School of Physics and Astronomy] | + | ** University of Nottingham |
| + | *** [http://www.nottingham.ac.uk/physics/ School of Physics and Astronomy] | ||
* Journals | * Journals | ||
** [http://www.iop.org/EJ/journal/JMM Journal of Micromechanics and Microengineering] | ** [http://www.iop.org/EJ/journal/JMM Journal of Micromechanics and Microengineering] | ||
** [http://www.ecmjournal.org/ European Cells & Materials Journal] | ** [http://www.ecmjournal.org/ European Cells & Materials Journal] | ||
| + | * [http://en.wikibooks.org/wiki/Nanowiki Wikibooks' Nanowiki] | ||
* [http://www.jeolusa.com/tem/temprods/fastem_faq.html JEOL USA FasTEM] | * [http://www.jeolusa.com/tem/temprods/fastem_faq.html JEOL USA FasTEM] | ||
* [http://www.links999.net/robotics/nanotechnology/index.html Links999 Nanotech Page] | * [http://www.links999.net/robotics/nanotechnology/index.html Links999 Nanotech Page] | ||
Revision as of 18:51, 13 July 2006
Contents |
The Nanorobotics Project
A large new nanotechnology research programme Nanorobotics - technologies for simultaneous multidimensional imaging and manipulation of nanoobjects is to be established at Sheffield University from Autumn 2004 funded by a £2.3Millon grant from the RCUK Basic Technology research programme. The programme led by the Engineering Materials Department oef the University of Sheffield, will be a collaboration between the University of Sheffield, Sheffield Hallam University and the University of Nottingham.
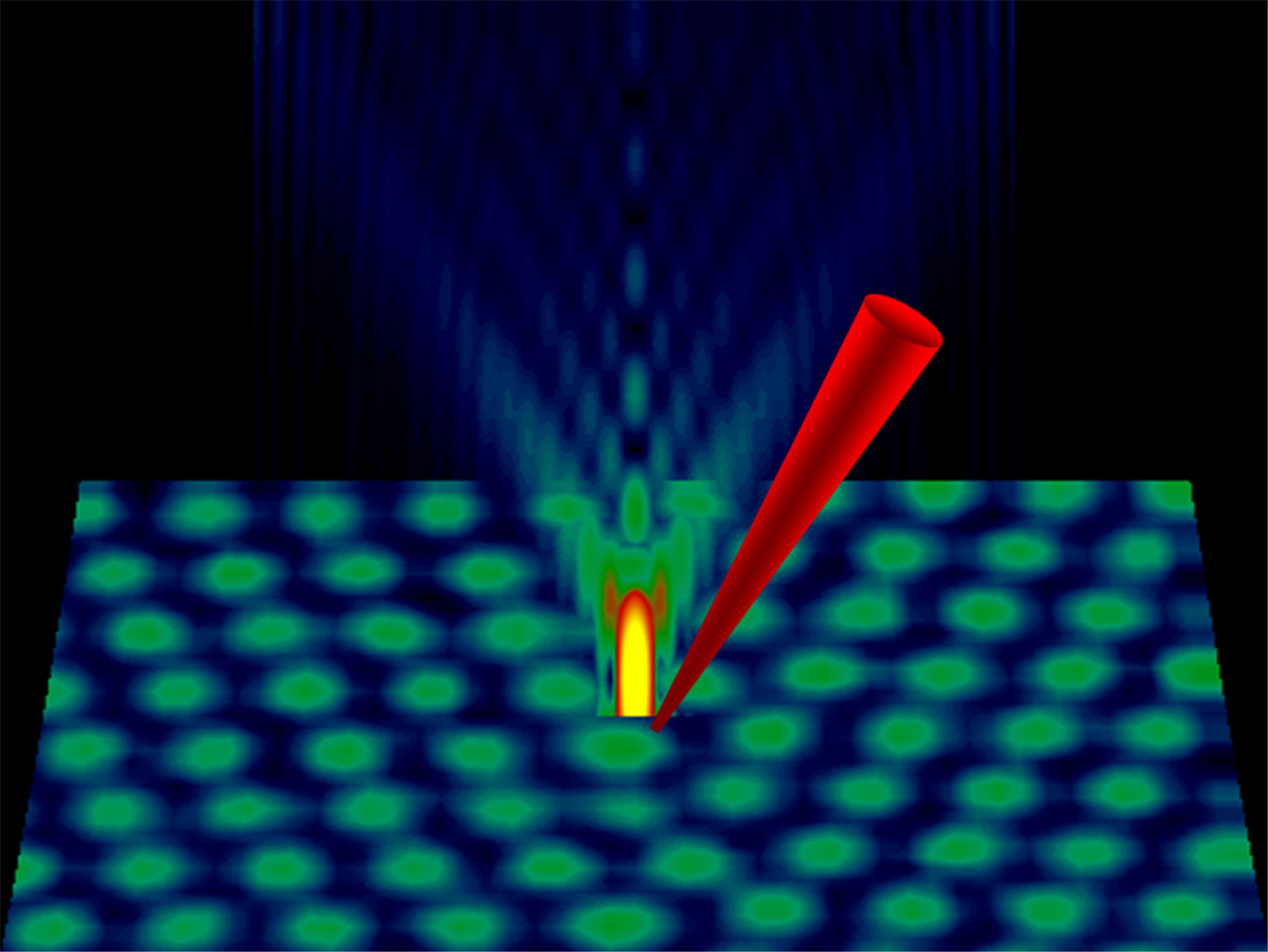
Many new nanotechnology research fields require a high degree of precision in both observing and manipulating materials at the atomic level. The advanced nanorobotics technology needed to manipulate materials at this scale, a million times smaller than a grain of sand, will be developed in the new Sheffield Nanorobotics group. The integration of different technologies to act as simultaneous real-time nanoscale "eyes" and "hands", including the advanced nanorobotics, high-resolution ion/electron microscopy, image processing/vision control and sophisticated sensors, will lead to the ability to manipulate matter at the scale of atoms or molecules.
The Nanorobotics programme will thus allow unique experiments to be carried out on the manipulation and observation of the smallest quantities of materials, including research into nanoscale electronic, magnetic and electromechanical devices, manipulation of fullerenes and nanoparticles, nanoscale friction and wear, biomaterials, and systems for carrying out quantum information processing.
MMVL
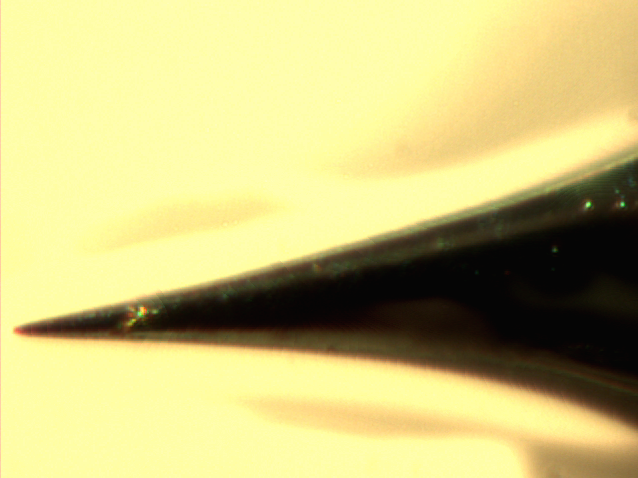
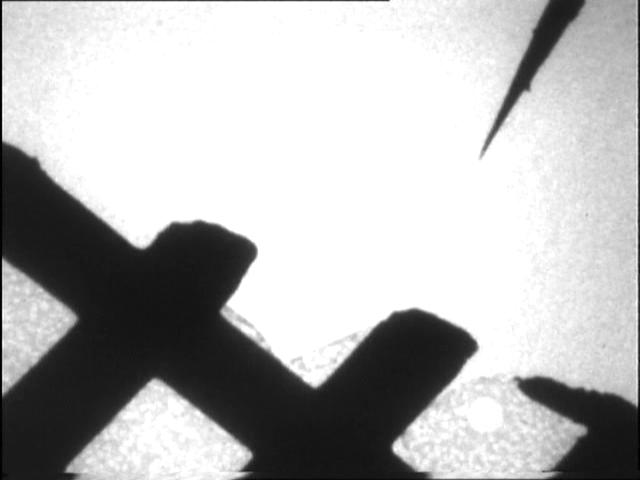
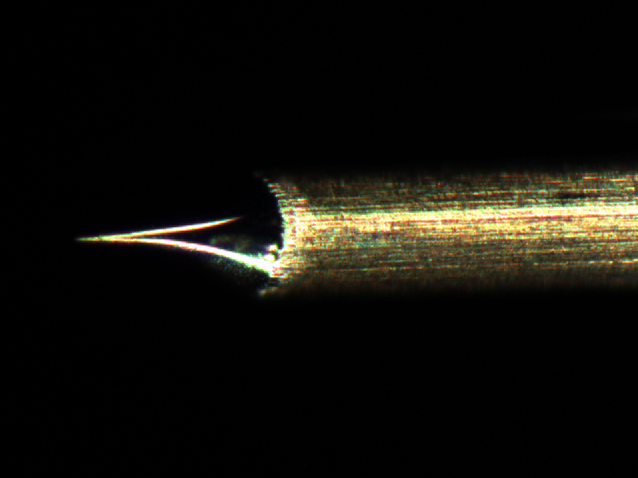
File:Tilt00.jpg TEM image of tungsten tip | |
File:Graphicaltip.png Graphical programming applied to indentation video |
The workpackage of the MMVL is to
- assist in hardness measurements by applying flow estimation on TEM videos
- provide real-time position feed-back for controlling the nano-indenter
- using input from S-Video- or alternatively Firewire-camera
- estimate x- and y-position of the tip
- estimate the depth of the tip using x- or y-image wobbling (this is a common technique for manually focussing on an object already)
- User-interface for telemanipulation and automated tasks
- Correlate AFM- with TEM-images
Further projects beyond the workpackage
- assist in hardness measurements by applying flow estimation on TEM videos
- estimation of optical flow
- automatise the measurements, which were done manually in context of this publication
- estimation of drift
- estimate movement of tip
- determine object-boundaries
See Also
- MMVL webdav server
- Registration of TEM images
- Realtime Linux
- Locating tungsten-tip by means of cross-correlation
- Structural Invariant Feature Transform
-
 Graphical Programming with Mimas and Qt-Designer
Graphical Programming with Mimas and Qt-Designer
External Links
- Project Partners
- Sheffield Hallam University
- University of Sheffield
- Project announcement
- University of Sheffield Engineering Faculty FEGTEM
- Publication Indentation mechanics of Cu-Be quantified by an in situ transmission electron microscopy mechanical probe
- Nanorobotics group at Sheffield University (project leader)
- University of Nottingham
- Journals
- Wikibooks' Nanowiki
- JEOL USA FasTEM
- Links999 Nanotech Page
- CAVIAR: Image-based recognition project
- TEM
- Nanorobotic Manipulation System at the Fukuda Lab
- Micro Stereo Litography
- An Introduction to Intelligent and Autonomous Control
- Fabry-Perot interferometer
- Overview of fiber-optical sensors
- Tomography with electron microscopes
- A to Z of nanotechnology
- Software
- Tomography with electron microscopes
- Nano-Hive Nanospace Simulator
- IMOD tomography software. (License doesn't allow redistribution of Source-code!)
- AMIRA 3D segmentation and visualisation (commercial software)
- CTSim: Computer Tomography Simulator
- Tomography at Queen Mary University of London
- Tomography demonstration at EPFL
- Gnome X Scanning Microscopy
- IMOD tomography software (proprietary license)
- SUGAR open source MEMS simulator