Interactive Presentation Software
m |
m |
||
| (9 intermediate revisions by one user not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
|- | |- | ||
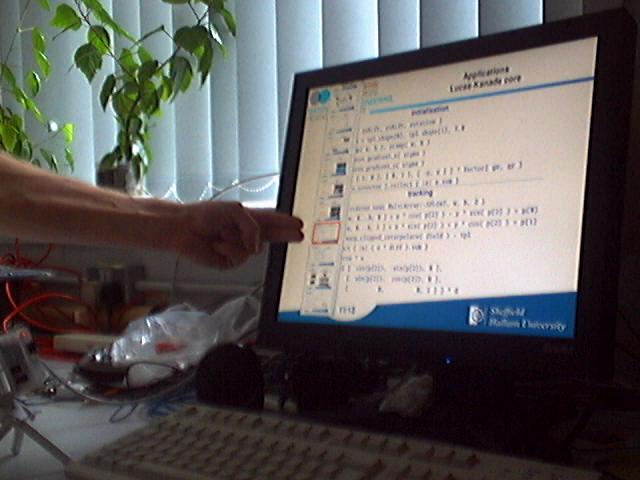
|[[Image:Rmando.jpg|thumb|320px|The interactive presentation software in action]] | |[[Image:Rmando.jpg|thumb|320px|The interactive presentation software in action]] | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
|} | |} | ||
| Line 12: | Line 9: | ||
'''RMando''' is a '''human computer interface''' based on the experience gained from the development of [[Interactive Camera-Projector System|KMando]]. | '''RMando''' is a '''human computer interface''' based on the experience gained from the development of [[Interactive Camera-Projector System|KMando]]. | ||
| − | The software | + | The software requires an IIDC/DCAM compatible firewire camera such as the [http://damien.douxchamps.net/ieee1394/cameras/ Unibrain Fire-i]. The camera is calibrated using Gray code sequences. The application allows you to load a set of images and display them as slides. After displaying a slide in fullscreen mode, a reference images is taken. User interaction is detected by computing difference pictures and counting the number occluded pixel in virtual sensor stripes located at the left and the right of the screen. |
==Downloads== | ==Downloads== | ||
| − | The implementation is little more than 1000 lines of Ruby code. The software is included in the | + | The implementation is based on the Ruby-extension [[HornetsEye]] and is little more than 1000 lines of Ruby code (plus a few GUI description files and icons). The software is included in the HornetsEye package as an [http://www.wedesoft.demon.co.uk/hornetseye-api/files/rmando-txt.html example program]. Note that the software currently only runs under GNU/Linux. |
==Possible Future Work== | ==Possible Future Work== | ||
* Improve user interface | * Improve user interface | ||
| + | * Support for Webcams (without support for manual exposure) | ||
=See Also= | =See Also= | ||
| Line 26: | Line 24: | ||
=External Links= | =External Links= | ||
* [http://www.wedesoft.demon.co.uk/hornetseye-api/files/rmando-txt.html HornetsEye webpage about RMando] | * [http://www.wedesoft.demon.co.uk/hornetseye-api/files/rmando-txt.html HornetsEye webpage about RMando] | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{Addthis}} | ||
[[Category:Projects]] | [[Category:Projects]] | ||
[[Category:Fun-Projects]] | [[Category:Fun-Projects]] | ||
Latest revision as of 21:08, 16 April 2011
Contents |
[edit] Interactive Presentation Software
[edit] Application
RMando is a human computer interface based on the experience gained from the development of KMando.
The software requires an IIDC/DCAM compatible firewire camera such as the Unibrain Fire-i. The camera is calibrated using Gray code sequences. The application allows you to load a set of images and display them as slides. After displaying a slide in fullscreen mode, a reference images is taken. User interaction is detected by computing difference pictures and counting the number occluded pixel in virtual sensor stripes located at the left and the right of the screen.
[edit] Downloads
The implementation is based on the Ruby-extension HornetsEye and is little more than 1000 lines of Ruby code (plus a few GUI description files and icons). The software is included in the HornetsEye package as an example program. Note that the software currently only runs under GNU/Linux.
[edit] Possible Future Work
- Improve user interface
- Support for Webcams (without support for manual exposure)